Food packaging is an integral part of food commodities. One of the major projects in the food industry process. It protects food and prevents the damage of biological, chemical, and physical external factors during the circulation of food from the factory to the hands of consumers. It also has the function of maintaining the stable quality of the food itself, and it is convenient for food consumption. It is the first to express the appearance of food and attract consumers. It has value beyond material costs. Therefore, the food packaging process is also an integral part of the food manufacturing system engineering.
Food packaging plays an important role in the industry, also it’s an indispensable presence in our life. Nowadays, more and more consumers choose green products. Thus, is undoubtedly an industry innovation for food packaging. From production standards to use standards, manufacturers have begun to focus on the development direction of eco-friendly protection and recycling technological innovation.
Let’s see the development of food packaging and the subsequent market situation! In order to boost your business, here are some key points you have to know about the food packaging industry!
Food packaging situation right now:
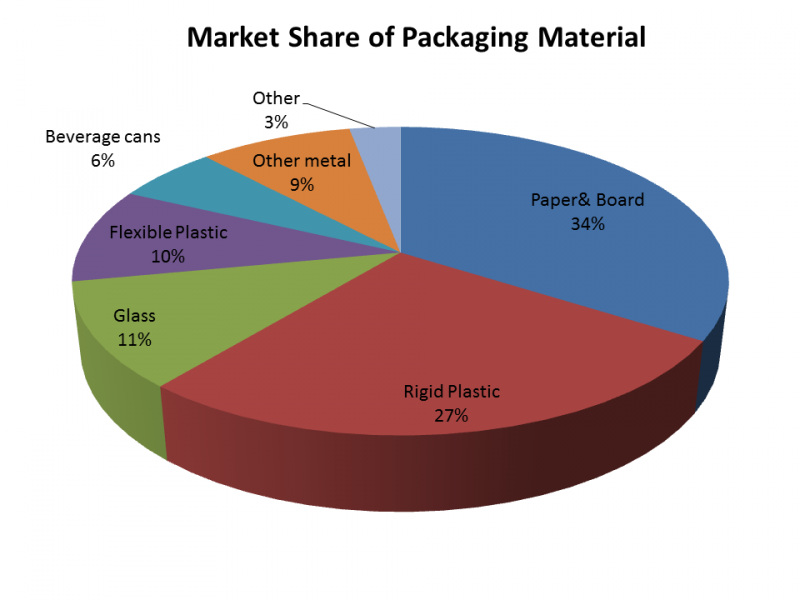
For some types of food packaging, the food contact material determines the name. A plastic bottle is made of plastic and has this material type in direct contact with the foodstuff. For glass jars, the materials in contact with the foodstuff are glass and coated metal from the closure.
In the case of beverage cartons, the direct food contact layer is not a carton, but laminated plastic. For aluminum cans, a coating is in direct contact with the beverage. Some types of paper can also be coated (for example with a grease-proof coating).
What are the requirements of food packaging in Australia?
If you’re a food business, it’s important to know what types of packaging are safe to use with your food products.
Under Standard 3.2.2 – Food Safety Practices and General Requirements, food businesses must:
- Only use packaging material that is fit for its intended purpose.
- Only use a material that is not likely to cause food contamination.
- Ensure there is no likelihood that the food may become contaminated during the packaging process.
Access the Food Packaging Infobite as a PDF here:
What are the requirements of food packaging in Australia?
If you’re a food business, it’s important to know what types of packaging are safe to use with your food products.
Under Standard 3.2.2 – Food Safety Practices and General Requirements, food businesses must:
- Only use packaging material that is fit for its intended purpose.
- Only use a material that is not likely to cause food contamination.
- Ensure there is no likelihood that the food may become contaminated during the packaging process.
Access the Food Packaging Infobite as a PDF here:
All Types of Food Packaging Material
Food packaging is widely used in our life. You may also know a lot about the materials and types of food packaging.
Food packaging material is an essential component of the food industry, as it helps to preserve and transport food items.
Packaging materials are available in a variety of materials such as metals, paper, and polymers. Each material has its own unique properties which make them suitable for different types of food products.
The use of packaging materials dates back to the early 19th century when glass jars were used to preserve food items.
Since then, advances in technology have enabled manufacturers to produce packaging materials with improved strength, durability, cost-effectiveness, and lless health risks.
Today’s packaging materials include everything from paper cartons and plastic wraps to aluminum cans and polyethylene bags.
Each material has its own unique properties which makes them suitable for different types of food products.




Cardboard, and papers:
Paper And Cardboard
Paper And Cardboard are other types of food packaging material. It is derived from renewable resources, has a low carbon footprint, and is biodegradable. Paper and board are versatile in terms of design and cost-effectiveness.
The advantages of using paper and board for food packaging include:
* Environmental benefits:
* Renewable resource
* Low carbon footprint
* Biodegradable
* Versatility:
* Wide range of designs available
* Cost-effective compared to other materials
* Safety:
* Non-toxic if disposed of properly
Paper and board are also relatively lightweight which makes them easy to transport and store.
Furthermore, depending on the type of paper or board chosen, it can be printed with various colors or designs that can make the product more appealing to potential customers.
In addition, some types of paper are treated with wax or plastic so they become moisture proof which is beneficial for wrapping foods that need to stay dry such as crackers.
However, there are some drawbacks when using paper and board for food packaging.
For example, they cannot be used in hot filling applications because they will not maintain their structure or shape when exposed to high temperatures.
Also, they may not provide enough protection against oxygen or moisture which can cause food spoilage over time.
Additionally, paper products can absorb grease or oils which could cause problems during the packaging process if not managed correctly.
Overall, paper and board offer many benefits for food packaging due to their environmental friendliness, versatility in design options, safety features, lightweight characteristics, and cost-effectiveness;
Wood
Wood is a traditional packaging material that provides a natural, sustainable, and biodegradable option.
It is strong, yet lightweight and can offer superior protection from environmental elements such as temperature and moisture.
In addition, wood has the ability to absorb odors, making it suitable for food packaging applications.
Wood can be easily manipulated into various shapes and sizes through cutting or shaping processes.
For example, wooden boxes can be made to fit any product size requirements and their walls can be customized with additional padding if needed.
Furthermore, wood may also be used in combination with other materials such as plastics or metal fastenings to create multi-layered packages.
Due to its strength and durability, wood is an ideal choice for long-term storage of goods.
Its natural characteristics also make it aesthetically appealing which is an advantage when creating attractive packaging designs.
Additionally, wooden packaging can help reduce distribution costs by providing reliable protection during the transportation process.
Plastics
Plastics are organic polymeric materials that can be molded into the desired shape. The lightness and versatility of these have been confirmed over decades in the processing and packaging of food. Plastic containers and packaging protect against the contamination of food and offer adequate mechanical strength.
Due to a lower cost and lower energy consumption during manufacturing, plastics have replaced traditional packaging materials. In addition, they are able to preserve and protect the food for longer, minimizing the use of preservatives.
In relation to the consumer, they are easy to handle and open and offer an effective surface for printing labels or brands. However, although plastics are recyclable materials, they are pollutants.
In the plastic manufacturing process, there are many varieties of plastic resins, with the most used being:
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): very resistant to humidity, fats and gases
Polyethylene and its varieties (PET, HDPE, LDPE). The development of the PET range has revolutionized the packaging industry, allowing plastic to compete directly with glass bottles.
Polystyrene (PS) is the plastic of choice for thermoforming due to its strength, malleability and low cost.
Metals (steel, tin, aluminum)
Metals are one of the most commonly used materials for food packaging.
They offer a number of advantages such as strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
Metals are also recyclable and can be easily reused after they are emptied.
Additionally, metals provide excellent barrier properties to protect the contents inside from oxygen, light, and moisture.
Commonly used metals for food packaging include tin-plated steel, aluminum foil, and foil laminates.
Tin-plated steel is a popular choice for cans and trays due to its strength and low cost.
It provides good protection against oxygen but requires an additional barrier layer to keep out moisture.
Aluminum foil is lightweight and provides excellent barrier properties against both oxygen and moisture while still being malleable enough to form various shapes.
Foil laminate materials combine aluminum foil with paper or plastic films for added protection against light or humidity.
The main use of these metals is the preservation of canned foods and beverages. The most commonly used are tin-coated steel and aluminum cans. It is an opaque material that provides an advantage for food that is sensitive to light.
Tin cans are made of steel sheets coated with tin as a measure of protection against corrosion of steel.
Aluminum is increasingly used for canning due to its lightness, low cost and capacity to be recycled. It can be found in packaging, bottle closures, and wraps, and laminates. It has the same barrier properties as steel but with the advantage of being resistant to corrosion.
Aluminum foil is formed by layers of laminated aluminum. It is a highly flexible product that allows to preservation or protect food in the domestic environment. However, it is difficult to use in modern fast packaging equipment due to wrinkles, rips, and marks.
Thin-walled aluminum cans are suitable for carbonated beverages, while wide-walled cans are suitable for steam sterilization. Optionally, internal lacquers can be used to avoid interaction with the product and externally to protect the ink from the labeling.
Glass
Glass is a popular packaging material for food items due to its longevity and unique aesthetic qualities.
It is strong, heat-resistant, and non-porous, which makes it suitable for storing various types of food products.
Additionally, glass containers provide an excellent barrier against oxygen, moisture, and light.
This ensures that food remains fresh for longer periods of time without compromising taste or nutritional value.
Furthermore, glass packaging is easy to clean and sterilize, making it ideal for use in a variety of settings including commercial kitchens and restaurants.
Glass food containers are also recyclable and reusable.
Consumers can use them again to store other items or return them to the manufacturer or local recycling center where they can be broken down into raw materials such as sand and recycled into new products.
Recycling glass reduces waste and conserves natural resources while still providing consumers with durable packages that preserve their food quality over time.
The benefits of glass packaging make it a logical choice for many food manufacturers looking to give customers safe, long-lasting products at an affordable price.
Its visually appealing qualities further add to its appeal as a practical material in the food industry
Glass containers can be bottles (the most used), jars, glasses, ampoules, jars, etc. However, this material is not used for frozen products due to the risk of breakage.
Ceramic
Ceramics are an important material used in food packaging.
They are a type of non-metallic inorganic compound, made up of metallic and non-metallic elements.
Ceramics have been around since Ancient times, and have been used to package food for centuries.
Characterized by their low thermal conductivity, high hardness, and chemical inertness, ceramics are highly resistant to heat and pressure. Moreover, they offer good physical strength and protection for the food product being packaged.
Foods that need to be kept at cold temperatures require special ceramic packaging materials due to their low thermal conductivity.
Examples of such foods include milk products, ice cream, frozen fruits, vegetables, and juices.
Ceramic packages also provide extra insulation from air and moisture which can cause spoilage or contamination of the food product inside.
Additionally, the use of specialized coatings on the outside surface of ceramic packages can help protect against microbial growth or leaching out of toxic substances from the package into the food product.
Due to their properties, ceramics are ideal materials for food packaging as they are able to provide a safe environment for storing and transporting foods while keeping them free from contaminants or spoilage agents.
As a result, they are often used in combination with other materials such as glass or plastic to create multi-layered packaging solutions that offer optimal protection for various types of foods.
Printing Inks
Printing inks are a key component in food packaging materials, providing the visual information that allows consumers to identify, select, and purchase products.
Inks can be formulated with a variety of components depending on their intended application.
The following table describes the three most common types of printing ink used in food packaging:
- Solvent-Based
Made from petroleum oil-based solvents, these inks have good adhesion to nonporous surfaces such as plastic or metal
Labels and graphics on PET containers, shrink sleeves
- Water-Based
Comprised of water-soluble resins, these inks are easy to clean up and eco-friendly Cartons and boxes for dry goods such as cereals, and snacks
- UV Curable
This type of ink cures instantly under ultraviolet light, forming an impermeable layer that resists abrasion and chemicals
Direct food contact labels for frozen products
In addition to providing product identification information, printing inks may also add functional properties to food packaging materials.
For example, metallic or fluorescent colors can be used for tamper evidence applications. In order to meet regulatory requirements for direct contact with food items, printing inks must also be certified as food safe.
Therefore it is important to consider the type of ink required when selecting a suitable material for a specific application.
Wax
Wax is an organic compound with a long history of use for preserving and coating foods.
It has a number of advantages over other materials, including its low cost, ease of application, and ability to repel moisture.
Wax also provides an effective barrier against oxygen and other gases that can cause spoilage.
The two most common types of wax used in food packaging are paraffin and beeswax.
Paraffin is derived from petroleum and is more affordable than beeswax, but it does not offer the same level of protection against moisture or gases.
Beeswax is made by bees and has been used for centuries to preserve food; it offers superior protection against moisture and gases but is more expensive than paraffin.
Wax-coated paper and cardboard are widely used for products such as cereal boxes, cracker boxes, snack bags, and candy wrappers.
The wax helps prevent water from seeping through the paper or cardboard, which can cause staining or discoloration over time.
As such, wax-coated paper and cardboard are ideal materials for food packaging that needs to be stored at room temperature or in humid conditions.
Moving on from wax, the next material to discuss when it comes to food packaging is wood.
Types of food packaging:

TYPES OF FOOD PACKAGING:
TRAYS AND
PUNNETS
Relatively shallow containers that may have a lid. They are used as food containers. There are plastic trays of all kinds: those used as a primary food-contact packaging, such as foamed, transparent, high-barrier, peelable, and reclosable trays, and those used as secondary packages, which are normally thermoformed for containing other food packages.

TYPES OF FOOD PACKAGING:
JARS
Rigid containers consisting of a round neck with a diameter similar to that of the body diameter and with a relatively large opening capable of supporting a lid to keep the product inside. The section of the body is usually round or square

TYPES OF FOOD PACKAGING:
FILM
A continuous and thin layer of plastic material with a small thickness. When the thickness is higher than approximately 250 microns, we do not consider it a film, but a sheet.
Bags
Bags offer a number of benefits for both retailers and consumers.
They are lightweight, relatively inexpensive, and easy to store compared to other forms of packaging.
Furthermore, they can be made with a variety of materials, such as plastic films or multi-layer films which provide additional protection against oxygen or moisture ingress.
The perforation and reliability features further enhance their utility, making them convenient for customers who wish to consume only part of a package at one time without having to repackage the remaining product or worry about spoilage due to exposure.
In addition, bags can also be custom printed with brand logos or product information that help attract attention on store shelves and create stronger brand recognition among customers.
Finally, they can also be produced in various sizes which makes them suitable for different markets by allowing producers to customize their packaging based on customer needs and preferences.
With these features considered, bags remain one of the most attractive forms of food packaging available today.
Box
Boxes are used to package a wide range of foods and food items.
They are generally made from cardboard but can also be produced from plastic or fiberboard.
Boxes come in various sizes and shapes, with the most common being rectangular or square.
Depending on its contents, a box may have one or more compartments either inside or outside of it.
Some boxes are designed to be opened and closed multiple times while others are meant to be single-use only.
The primary benefit of using boxes for food packaging is that they provide a secure method of protecting the product without adding too much weight or bulkiness.
This is especially important when it comes to products that are fragile or require extra care during shipping.
Additionally, boxes can be printed with logos and other marketing materials which can help increase brand awareness and recognition when selling online.
Finally, they offer an economical option for businesses looking to reduce their packaging costs while still providing a safe and secure solution for their products.
Cans
Cans are one of the most common types of food packaging.
They are made from thin sheets of metal that have been rolled into a cylinder shape and then sealed at either end with an airtight lid.
Can offer a number of advantages over other forms of packaging:
* Cost-effective: Cans are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and can be used to package a wide variety of products.
* Convenient: Cans are easy to store and transport, as well as being lightweight and stackable.
* Durable: Cans are strong and durable, making them ideal for long-term storage and shipping.
Can provide an effective barrier against oxygen, light, and moisture which helps maintain the quality, freshness, and safety of the food.
The interior is often lined with a protective coating to prevent corrosion or contamination from the metal container itself.
As such, cans are well suited for preserving foods with extended shelf lives.
Can also come in a variety of sizes, shapes, colors, and materials which can help distinguish one product from another on store shelves. This makes them an attractive choice for marketing purposes as well as packaging.
Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging offers numerous advantages over cartons and other types of food packaging
Flexible packaging is usually made from materials such as plastic, metalized film, or paper-based structures with a plastic or wax barrier.
It can be used for a variety of items such as snacks, cereals, and even liquid products like milk and juice.
The main advantage of flexible packaging is that it takes up less space than traditional rigid containers making it easier to store and ship.
Additionally, it weighs less than cartons which further reduces shipping costs.
Flexible packaging also offers a number of other benefits including improved product visibility, longer shelf life due to better barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and light, affordability compared to other forms of food packaging, and excellent printability for branding purposes.
Furthermore, it is more environmentally friendly since it uses significantly less energy in production than traditional rigid containers.
The ease of use associated with flexible packages makes them ideal for a wide range of applications ranging from retail to food service operations.
Inspiration packaging design in life
When you go to the supermarket, the most attractive product on the shelves is the packaging. Therefore, the unique packaging design is important. Here, we have collected a lot of special food packaging design for you, which one can inspire you?
With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, three major points of recyclable, degradable and recyclable will become the development trend of the packaging industry. So what is the green development prospect of food packaging?
Three Sustainability Trends Reshaping the Food Packaging Industry
Corporate leaders are embracing sustainable food and beverage packaging
A key food packaging trend in 2018 has been toward recycled and recyclable materials, partly in response to stunning media reports of waste plastic, notably the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (three times the size of France).
Beyond plastics, leading beverage and restaurant brands have answered the call and announced major sustainability-oriented commitments in 2018. The trend-setters include:
Coca Cola stated that by 2030 it will collect and recycle one bottle or can for each one it sells; and
McDonald’s announced a commitment to have 100% of its guest packaging made from renewable, recycled or certified sources by 2025.
These actions have pleased everyday consumers as well as committed environmentalists, and will have trickle-down effects, encouraging other companies to follow.
Governments are not only banning plastic, but mandating recycling and reusable materials
In Australia, national, state and territory environment ministers have agreed on an admirable target: 100% of Australian packaging is to be recyclable, compostable or reusable by 2025. This is only a few short years away, and a major opportunity for the food packaging industry.
The worldwide trend is clear on the legislative front: Less in the way of plastics and single use materials, more in the way of recycling and sustainable food packaging.
Innovative and sustainable food packaging is creating new solutions
Innovative recycled and recyclable food packaging materials are emerging as sustainable alternatives to plastics, Styrofoam and other environmentally-unfriendly materials. Such as Kraft paper packaging and pp woven bags currently used in the market.
Benefits of food packaging
In previous chapters the reasons why used food packaging has been described in detail. Here we have summarise several key poins of the benefits of food packaging! These benefits include:
– improved protection for the food and an increased shelf-life,
– better quality products reaching the consumer,
– more attractive products to compete with other manufacturers,
– easily identifiable products for consumers to select from retail shops,
– sometimes re-usable containers,
– tamperproof packages reduce the risk of adulteration,
– making foods more easily handled and stored by retailers and consumers,
– increased production output as a longer shelf-life enables a larger market to be found and year-round production possible.
What Is The Most Cost-Effective Type Of Food Packaging?
The most cost-effective type of food packaging is an important consideration for businesses seeking to reduce their overhead.
Packaging materials can represent a significant portion of the total costs associated with a product, so understanding the various options and their associated expenses is key to making the best decision.
In this article, we will discuss some of the most cost-effective types of food packaging available today.
1. Cardboard
Cardboard is one of the most affordable and versatile materials used in food packaging today.
It can be easily printed with a variety of branding and labeling options, and it is also lightweight and durable. Furthermore, cardboard is recyclable, which helps reduce waste and contributes to sustainability efforts.
2. Plastic
Plastic is another popular material used for food packaging due to its affordability and versatility.
It can come in a variety of forms such as pouches, trays, and tubs that provide protection for products during shipping or storage.
Additionally, plastic can be manufactured into containers with different shapes that conform to specific product requirements for presentation purposes.
3. Glass
Glass is also an effective material for food packaging because it does not contain any chemicals that could leach into food products or affect their flavor or texture negatively.
Plus, glass containers are easily recycled if they are disposed of properly and safely collected from landfills or other sources.
4. Aluminum: Aluminum provides an excellent barrier against moisture, oxygen, light, and odors while still being lightweight and relatively inexpensive compared to other materials like glass or plastic.
Aluminum containers are reusable after being washed thoroughly with warm water and soap making them both economical and sustainable options for many businesses today.
In addition to these four primary types of materials used in food packaging today, there are also other more specialized mediums such as biodegradable plastics that may be suitable depending on individual needs or preferences.
Ultimately though when selecting a material for food packaging it’s important to consider all factors including budget constraints as well as environmental impact before making a final decision in order to ensure the most cost-effective solution possible without sacrificing quality or safety standards.
What Types Of Food Packaging Are Best For Preserving Food?
Food packaging is an important consideration for those looking to preserve the freshness of their food.
It helps to protect food from spoilage, contamination, and other external influences that can damage it over time. In order to best preserve food, it is important to consider which types of food packaging are most suitable for the particular type of food being stored.
Various materials are used in the production of food packaging, each with its own set of properties that make it well-suited for various applications. Common materials used in food packaging include plastics, paper and cardboard, metals, glass, and biodegradable substances.
Depending on the desired length of preservation and other considerations such as price-point or environmental impact, one material may be more suitable than another.
For example, plastic is a popular choice due to its low cost and durability. However, plastic containers can leach chemicals into foods over time or even become brittle if mishandled or exposed to extreme temperatures which could lead to spoilage.
Paper and cardboard are lightweight and easy to recycle but may not provide adequate protection from moisture or oxygen which could lead to mold growth or oxidation of compounds in the food product.
Metals offer excellent protection but require specialized equipment for sealing and do not offer any insulation from temperature variations.
Glass offers good heat resistance but can be fragile if mishandled, making it difficult to transport without risk of breakage.
Biodegradable materials offer an environmentally-friendly option but may not provide adequate protection from external factors such as humidity or sunlight which could degrade the food product over time.
Considering these factors when selecting a type of food packaging can help ensure that the desired level of preservation is achieved while also accounting for cost-effectiveness and sustainability concerns as needed.
By taking into account all relevant variables when making this decision consumers can ensure they have chosen a packaging solution that will effectively preserve their desired food product while also being safe and responsible with regard to environmental impacts associated with its use.
Conclusion:
Consumers everywhere are increasingly looking at companies and brands to take the lead on environmental issues. And, as outlined above, the broad legislative trend toward bans and restrictions on unsustainable materials is encouraging the adoption of sustainable materials and practices.
For the food, beverage and restaurant industries, environmentally-friendly post-consumer recycled products can reduce environmental impact and contribute to the development of a truly sustainable economy, aligned trends.
Why choose PrimePac ?
At PrimePac, we bring together design experts and brand innovators to create fresh ideas, customized packages, and fully efficient processes.
We design creative packaging solutions that cater to a diverse global audience with the in-house knowledge and network of experienced professionals to meet the demands of every type of client.
From our dedicated sales team and warehouse staff in Australia to the experts at our production facilities in China, all of our employees are guided by four core values at the heart of our business: integrity, innovation, passion, and engagement.